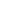
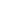The structural components of an electrical discharge machining (EDM) machine.
Release time:
2022-03-18
The structure of the electrical discharge machining (EDM) machine includes the bed, column, shaft, and worktable, primarily used for clamping and adjusting the tool and workpiece. The machine body needs to have sufficient rigidity to prevent deformation during the machining process, which could lead to changes in the discharge gap and hinder the machining process.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) Machine ToolThe structure includes the bed, column, spindle, and worktable, mainly used for clamping and adjusting tools and workpieces. The machine body needs to have sufficient rigidity to prevent changes in discharge gap due to deformation during processing, which would hinder machining. During the electrical discharge machining process, the tool electrode and workpiece are immersed in the working fluid. The main function of the working fluid is to compress the spark channel during discharge, concentrating the current in a small localized area to restore insulation and prevent arcing. The working fluid can also cool the tool and workpiece. To timely discharge the products of electro-corrosion, the EDM machine tool is also equipped with a working fluid circulation system that utilizes forced circulation of the working fluid.
Bed and Column: The bed and column are the basic structures that ensure the relative position of the electrode to the worktable and workpiece. Their precision directly affects machining. If the precision of the EDM machine tool is not high, it is difficult to guarantee machining accuracy. Therefore, not only should the structure of the bed and column be reasonable and have high rigidity to withstand the spindle load and the inertial forces from sudden acceleration of moving parts, but they should also minimize deformation caused by temperature changes, eliminate internal stress in a timely manner, and remain stable over long periods.
Worktable: The worktable is mainly used to support and clamp the workpiece. In actual processing, the relative position of the electrode and workpiece is changed by rotating vertical and horizontal screws. The upper part of the worktable is also equipped with a working fluid tank to hold the working fluid, allowing the electrode and workpiece to be immersed in the working fluid for cooling and chip removal. The worktable is a component that operators frequently move during clamping, using two handwheels to move the upper and lower sliding plate, changing the vertical and horizontal positions to meet the relative position between the electrode and workpiece. The types of worktables can be divided into: ordinary worktable and precision worktable.
This concludes today's introduction to electrical discharge machining machine tools. Thank you for your patient reading!
Related News